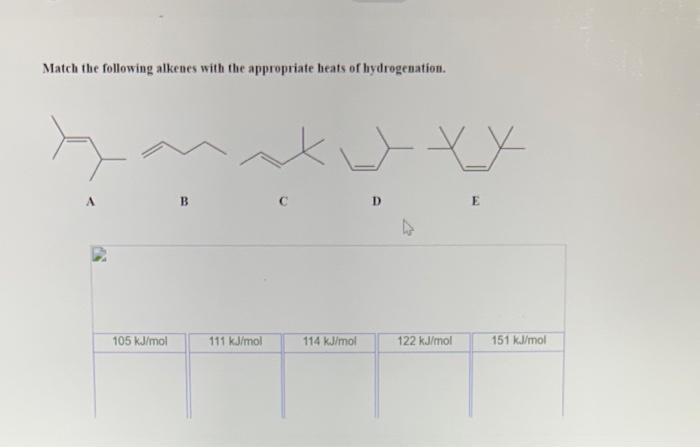
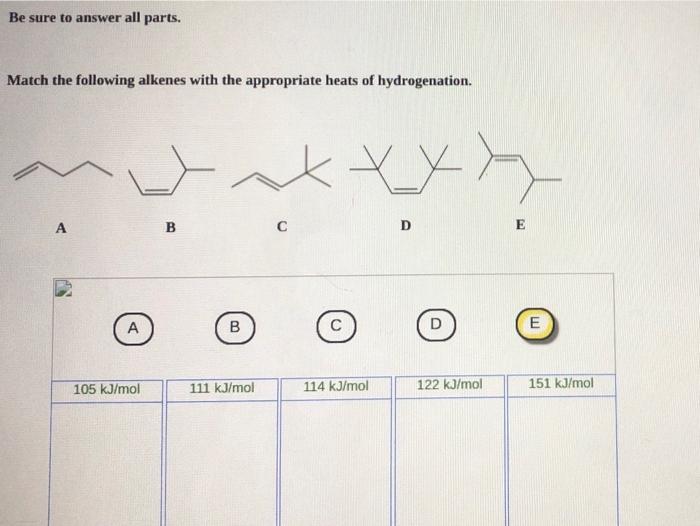
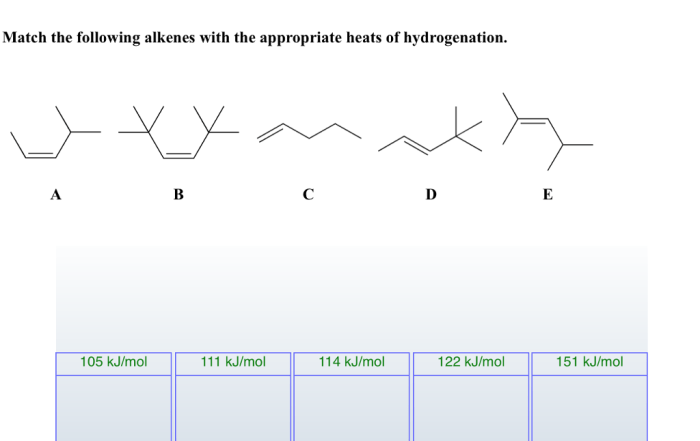
Match the following alkenes with the appropriate heats of hydrogenation. The heats of hydrogenation of alkenes are a measure of the stability of the alkene. The more stable the alkene, the lower the heat of hydrogenation. Factors that affect the heat of hydrogenation include the degree of substitution of the double bond, the presence of substituents, and the hybridization of the carbon atoms involved in the double bond.
Alkenes and Heats of Hydrogenation
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. The addition of hydrogen to an alkene, a process known as hydrogenation, results in the formation of a saturated alkane. The heat released during this reaction is known as the heat of hydrogenation.
The heat of hydrogenation is a measure of the stability of an alkene. More stable alkenes have lower heats of hydrogenation, while less stable alkenes have higher heats of hydrogenation.
Factors Affecting the Heats of Hydrogenation of Alkenes, Match the following alkenes with the appropriate heats of hydrogenation
- Number of double bonds:The more double bonds an alkene has, the higher its heat of hydrogenation. This is because each double bond requires the addition of two hydrogen atoms, which releases more heat than the addition of one hydrogen atom to a single bond.
- Type of double bond:Double bonds can be either cis or trans. Cis double bonds have the two hydrogen atoms on the same side of the double bond, while trans double bonds have the two hydrogen atoms on opposite sides of the double bond.
Cis double bonds have higher heats of hydrogenation than trans double bonds.
- Substitution:The presence of substituents on the alkene can also affect the heat of hydrogenation. Substituents that donate electrons to the double bond, such as alkyl groups, lower the heat of hydrogenation. Substituents that withdraw electrons from the double bond, such as halogen atoms, raise the heat of hydrogenation.
Matching Alkenes with Heats of Hydrogenation: Match The Following Alkenes With The Appropriate Heats Of Hydrogenation
| Alkene | Heat of Hydrogenation (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| Ethene | 125 |
| Propene | 119 |
| 1-Butene | 116 |
| cis-2-Butene | 117 |
| trans-2-Butene | 120 |
The table above shows the heats of hydrogenation for a variety of alkenes. The heats of hydrogenation increase as the number of double bonds in the alkene increases. Cis double bonds have higher heats of hydrogenation than trans double bonds.
The presence of substituents on the alkene can also affect the heat of hydrogenation.
Applications of Heats of Hydrogenation
Heats of hydrogenation have a number of applications in organic chemistry.
- Determining the stability of alkenes:The heat of hydrogenation can be used to determine the relative stability of alkenes. More stable alkenes have lower heats of hydrogenation, while less stable alkenes have higher heats of hydrogenation.
- Predicting the products of hydrogenation reactions:The heat of hydrogenation can be used to predict the products of hydrogenation reactions. Alkenes with lower heats of hydrogenation are more likely to be hydrogenated to form cis products, while alkenes with higher heats of hydrogenation are more likely to be hydrogenated to form trans products.
- Characterizing alkenes:The heat of hydrogenation can be used to characterize alkenes. By measuring the heat of hydrogenation of an alkene, it is possible to determine the number of double bonds, the type of double bond, and the presence of any substituents.
Limitations of Heats of Hydrogenation
While heats of hydrogenation are a useful tool for analyzing alkenes, there are some limitations to their use.
- Heats of hydrogenation are not always accurate:The heat of hydrogenation can be affected by a number of factors, such as the solvent used and the presence of impurities. This can make it difficult to obtain accurate heats of hydrogenation.
- Heats of hydrogenation are not always diagnostic:The heat of hydrogenation can only provide information about the relative stability of alkenes. It cannot be used to determine the absolute stability of an alkene.
Despite these limitations, heats of hydrogenation are a valuable tool for analyzing alkenes. They can be used to determine the relative stability of alkenes, predict the products of hydrogenation reactions, and characterize alkenes.
FAQ Compilation
What is the heat of hydrogenation?
The heat of hydrogenation is the amount of heat released when one mole of an alkene is hydrogenated to form one mole of the corresponding alkane.
What factors affect the heat of hydrogenation of alkenes?
The heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is affected by the degree of substitution of the double bond, the presence of substituents, and the hybridization of the carbon atoms involved in the double bond.
How can the heats of hydrogenation of alkenes be used to determine the stability of alkenes?
The heats of hydrogenation of alkenes can be used to determine the stability of alkenes because the more stable the alkene, the lower the heat of hydrogenation.
