Dc theory level 2 lesson 8 introduction to test instruments – Embark on an illuminating journey through the world of DC theory, as we delve into the fundamentals of test instruments in Lesson 8. Discover their vital role in various fields and explore the diverse range of applications that make them indispensable tools for electrical professionals.
Our exploration will uncover the basic principles that govern the operation of test instruments, shedding light on concepts such as accuracy, precision, resolution, and range. We will delve into the different types of test instruments, categorizing them based on their functionality and applications, and providing examples of each type, including multimeters, oscilloscopes, and signal generators.
1. Test Instruments
General Overview
Test instruments are indispensable tools in various fields, enabling the precise measurement and analysis of electrical, electronic, and physical phenomena. They play a crucial role in scientific research, engineering, manufacturing, and maintenance, providing valuable insights into system performance, fault detection, and troubleshooting.
Common test instruments include multimeters, oscilloscopes, signal generators, and spectrum analyzers. Multimeters measure voltage, current, and resistance, while oscilloscopes visualize electrical signals over time. Signal generators produce specific waveforms for testing circuits, and spectrum analyzers analyze the frequency and amplitude components of signals.
2. Basic Principles of Test Instruments

Test instruments operate based on fundamental principles that ensure accurate and reliable measurements. These principles include:
- Accuracy:The closeness of a measurement to the true value.
- Precision:The consistency of repeated measurements.
- Resolution:The smallest change in a measurement that can be detected.
- Range:The span of values that an instrument can measure.
3. Types of Test Instruments
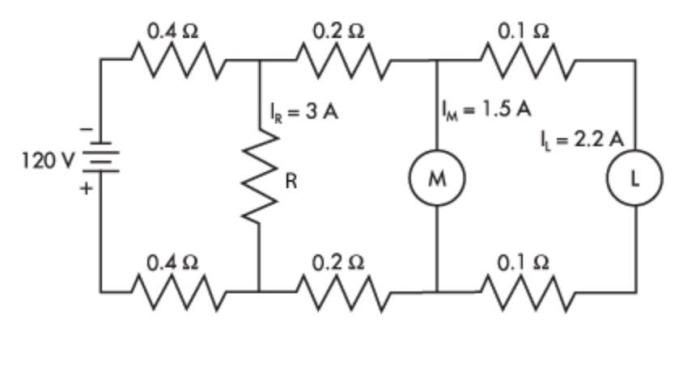
Test instruments are categorized based on their functionality and applications. Major types include:
- Multimeters:Measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Oscilloscopes:Visualize electrical signals over time.
- Signal generators:Produce specific waveforms for testing circuits.
- Spectrum analyzers:Analyze the frequency and amplitude components of signals.
- Data loggers:Record and store data over time.
4. Test Instrument Specifications: Dc Theory Level 2 Lesson 8 Introduction To Test Instruments
When selecting test instruments, it is crucial to consider key specifications that affect their performance. These specifications include:
- Accuracy:The percentage of error in measurements.
- Bandwidth:The range of frequencies an instrument can measure or generate.
- Input impedance:The resistance or capacitance presented by an instrument to the circuit being tested.
- Resolution:The smallest change in a measurement that can be detected.
- Sensitivity:The minimum signal level an instrument can detect.
5. Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when using test instruments. Proper handling, storage, and maintenance are essential to prevent accidents and ensure reliable operation. Key safety guidelines include:
- Use appropriate test leads:Ensure test leads are rated for the voltage and current being measured.
- Ground instruments:Connect instruments to a proper ground to prevent electrical shocks.
- Wear personal protective equipment:Use safety glasses, gloves, and appropriate clothing when working with high voltages or currents.
- Store instruments properly:Keep instruments in dry, dust-free environments when not in use.
- Calibrate instruments regularly:Ensure instruments are calibrated to maintain accuracy and reliability.
6. Troubleshooting Test Instruments
Test instruments may encounter problems during use. Common troubleshooting techniques include:
- Check connections:Verify that all connections are secure and free of corrosion.
- Inspect batteries:Replace weak or dead batteries.
- Clean probes and terminals:Use isopropyl alcohol to clean probes and terminals to ensure good contact.
- Check fuses:Replace blown fuses with the correct type and rating.
- Consult user manuals:Refer to user manuals for specific troubleshooting guidance.
7. Advanced Applications of Test Instruments
Beyond basic measurements, test instruments have advanced applications that expand their capabilities. These applications include:
- Signal analysis:Analyze complex signals to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Data logging:Record and store data over time for analysis and monitoring.
- Remote monitoring:Monitor instruments and data remotely for real-time insights.
- Automated testing:Use instruments in automated test systems for efficient and repeatable testing.
- Quality control:Utilize instruments to ensure product quality and compliance with standards.
Questions Often Asked
What are the most common types of test instruments?
Multimeters, oscilloscopes, signal generators, and power supplies are among the most commonly used test instruments.
What is the difference between accuracy and precision?
Accuracy refers to the closeness of a measurement to the true value, while precision refers to the consistency of repeated measurements.
How do I ensure safety when using test instruments?
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions, wear appropriate safety gear, and be aware of potential hazards such as electrical shock and arc flash.