Heart failure with atrial fibrillation hesi case study is a comprehensive analysis of a patient’s journey through this complex condition, providing valuable insights into its pathophysiology, diagnosis, management, and nursing care.
This in-depth exploration delves into the intricate details of heart failure with atrial fibrillation, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and potential complications.
Overview of Heart Failure with Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
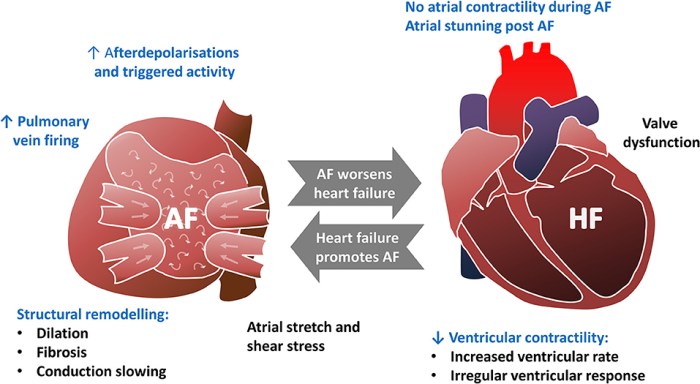
Heart failure with atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common and serious condition characterized by the presence of both heart failure and atrial fibrillation. Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, while atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heart rhythm that originates in the atria, the upper chambers of the heart.
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of heart failure with AF is complex and involves multiple factors. In heart failure, the heart muscle becomes weakened or damaged, leading to reduced pumping ability. This can be caused by various underlying conditions, such as coronary artery disease, hypertension, or cardiomyopathy.
Atrial fibrillation, on the other hand, is caused by abnormal electrical impulses in the atria. These impulses disrupt the normal coordinated contraction of the atria, leading to irregular and often rapid heartbeats. The combination of heart failure and AF can further worsen the heart’s function and increase the risk of complications.
Signs and Symptoms
- Shortness of breath, especially with exertion or lying down
- Fatigue and weakness
- Edema (swelling) in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
Risk Factors
- Age (over 65 years)
- Coronary artery disease
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sleep apnea
- Thyroid disorders
- Alcohol abuse
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis: Heart Failure With Atrial Fibrillation Hesi Case Study
Clinical Presentation
Patients with heart failure and AF may present with a variety of symptoms, including those described above. The physical examination may reveal signs of heart failure, such as jugular venous distension, edema, and rales in the lungs. The heart rate may be rapid or irregular, and a heart murmur may be present.
Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnosis of heart failure with AF is based on a combination of clinical findings, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
- History and physical examination:The patient’s history and physical examination can provide important clues to the diagnosis.
- Electrocardiography (ECG):An ECG can show the presence of atrial fibrillation and other heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Echocardiography:An echocardiogram can assess the structure and function of the heart, including the ejection fraction (EF), which is a measure of the heart’s pumping ability.
- Blood tests:Blood tests can be used to check for underlying conditions that may contribute to heart failure, such as anemia or thyroid disorders.
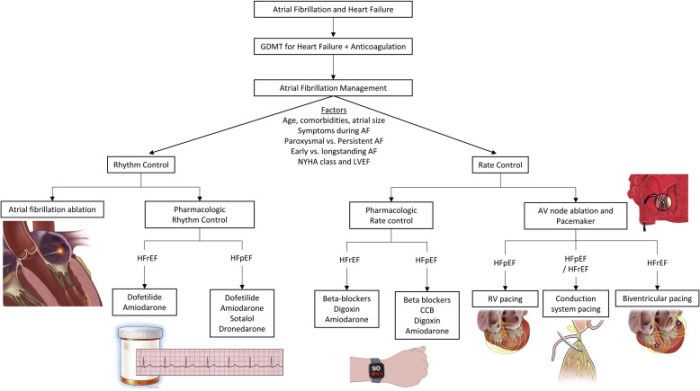
Management and Treatment Options
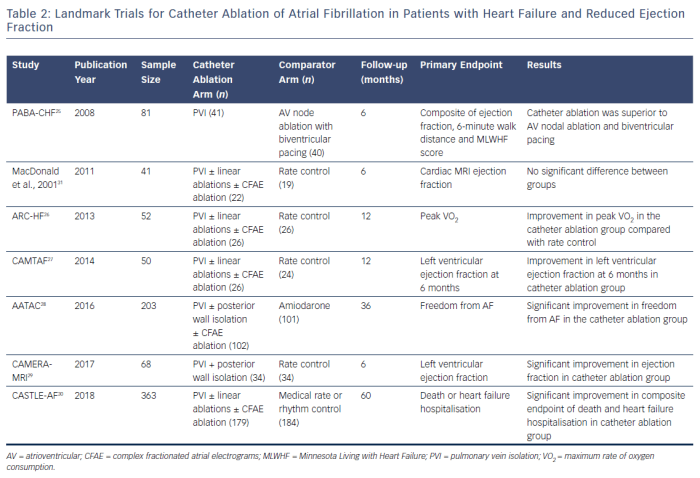
Goals of Treatment
The goals of treatment for heart failure with AF are to improve symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and improve survival. Treatment typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes device therapy or surgery.
Pharmacological Treatment Options
- Diuretics:Diuretics help to remove excess fluid from the body, reducing symptoms of fluid overload.
- ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs):These medications help to lower blood pressure and reduce the workload on the heart.
- Beta-blockers:Beta-blockers slow the heart rate and reduce the force of contraction, which can improve symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
- Digoxin:Digoxin is a medication that can help to slow the heart rate and improve heart function.
- Anticoagulants:Anticoagulants are medications that help to prevent blood clots, which are a common complication of atrial fibrillation.
Non-Pharmacological Treatment Options, Heart failure with atrial fibrillation hesi case study
- Lifestyle modifications:Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and weight loss, can help to improve heart health and reduce symptoms of heart failure.
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT):CRT is a device therapy that can help to improve the coordination of the heart’s contractions, which can improve heart function and reduce symptoms.
Nursing Care and Management
Role of Nurses
Nurses play a vital role in the care and management of patients with heart failure and AF. They are responsible for assessing the patient’s condition, providing education and support, and coordinating care with other members of the healthcare team.
Nursing Assessment
The nursing assessment of a patient with heart failure and AF should include:
- History and physical examination:A thorough history and physical examination can provide important information about the patient’s symptoms, underlying conditions, and risk factors.
- Assessment of vital signs:Vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate, can provide clues to the patient’s overall health and well-being.
- Assessment of fluid status:Nurses should assess the patient for signs of fluid overload, such as edema, jugular venous distension, and rales in the lungs.
Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions for patients with heart failure and AF include:
- Monitoring vital signs and fluid status:Nurses should monitor the patient’s vital signs and fluid status closely to assess for changes that may indicate a worsening condition.
- Administering medications:Nurses are responsible for administering the patient’s medications as prescribed.
- Providing education and support:Nurses should provide education and support to the patient and their family about heart failure and AF, including the importance of lifestyle modifications and medication adherence.
- Coordinating care:Nurses work with other members of the healthcare team to coordinate the patient’s care, including referrals to specialists, dietitians, and physical therapists.
Case Study Analysis
Case Study
A 75-year-old male patient presents to the clinic with a history of heart failure and atrial fibrillation. He has been experiencing increasing shortness of breath, fatigue, and edema in his legs and ankles. His past medical history includes hypertension and coronary artery disease.
On examination, the patient is in mild respiratory distress. His heart rate is 110 beats per minute and irregular, and his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg. He has jugular venous distension, edema in his legs and ankles, and rales in the lungs.
An ECG shows atrial fibrillation, and an echocardiogram reveals an ejection fraction of 35%. The patient is diagnosed with heart failure with atrial fibrillation.
Treatment Plan
The patient’s treatment plan includes:
- Medications:Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and digoxin
- Lifestyle modifications:Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and weight loss
Management Strategies
The patient’s management strategies include:
- Close monitoring of vital signs and fluid status
- Regular follow-up appointments
- Patient education and support
Evaluation
The patient’s response to treatment is evaluated through regular follow-up appointments. His symptoms have improved, and his vital signs and fluid status are stable. He is adhering to his medications and lifestyle modifications.
The patient’s ongoing care plan includes continued monitoring, medication management, and patient education and support to help him manage his condition and improve his quality of life.
FAQs
What are the common signs and symptoms of heart failure with atrial fibrillation?
Shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, irregular heartbeat, and chest pain.
What are the risk factors for developing heart failure with atrial fibrillation?
Age, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, smoking, and a family history of heart failure.
What are the goals of treatment for heart failure with atrial fibrillation?
To relieve symptoms, improve heart function, prevent blood clots, and reduce the risk of complications.