Label all the features of this fluvial landscape. This guide delves into the intricacies of fluvial landscapes, exploring their defining characteristics, diverse landforms, and ecological significance. Join us as we uncover the processes that shape these dynamic environments and examine the human impact on their delicate balance.
Fluvial landscapes, shaped by the relentless flow of rivers, exhibit a captivating array of features that tell the story of their formation and evolution. From meandering rivers to oxbow lakes and floodplains, each element plays a crucial role in the ecological tapestry of these landscapes.
Fluvial Landscapes: Key Features and Ecological Importance
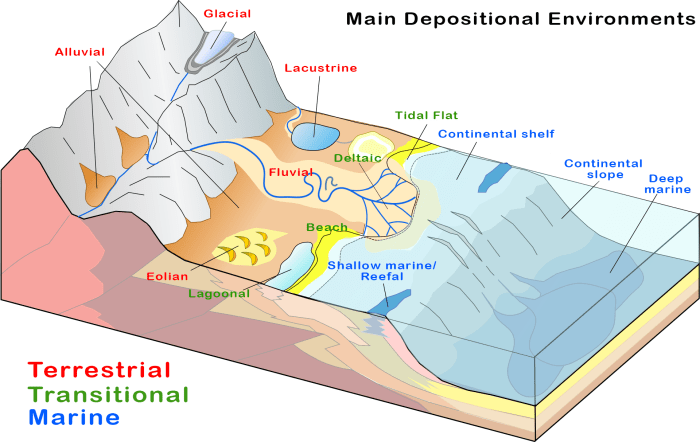
Fluvial landscapes, shaped by the erosive power of rivers, are dynamic environments characterized by distinctive features and ecological significance. Understanding these landscapes requires an examination of their main features, landforms, processes, ecological roles, and human impacts.
1. Identify the Main Features of a Fluvial Landscape
Fluvial landscapes are defined by several key features:
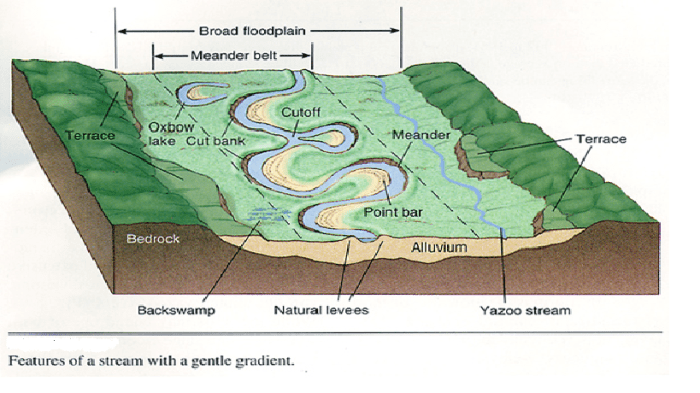
- Rivers:The primary agents of erosion and deposition, rivers transport sediment and shape the landscape.
- Floodplains:Flat, low-lying areas adjacent to rivers, prone to flooding during high flows.
- Levees:Natural embankments formed by sediment deposits along river banks, providing protection from flooding.
- Meanders:Sinuous bends in a river’s course, formed by erosion on the outer banks and deposition on the inner banks.
- Oxbow Lakes:Former meanders that have been cut off from the main river channel, creating isolated bodies of water.
- Terraces:Flat, elevated areas along river valleys, representing former floodplain levels.
2. Analyze the Different Types of Fluvial Landforms
Fluvial processes create a variety of landforms:
Meanders
Meanders are sinuous bends in a river’s course, resulting from erosion on the outer banks and deposition on the inner banks. They play a crucial role in creating diverse habitats and enhancing biodiversity.
Oxbow Lakes
Oxbow lakes are former meanders that have been cut off from the main river channel, creating isolated bodies of water. They provide important habitats for aquatic species and support diverse plant communities.
Floodplains
Floodplains are flat, low-lying areas adjacent to rivers, prone to flooding during high flows. They act as natural flood buffers, reducing downstream flooding and enhancing soil fertility.
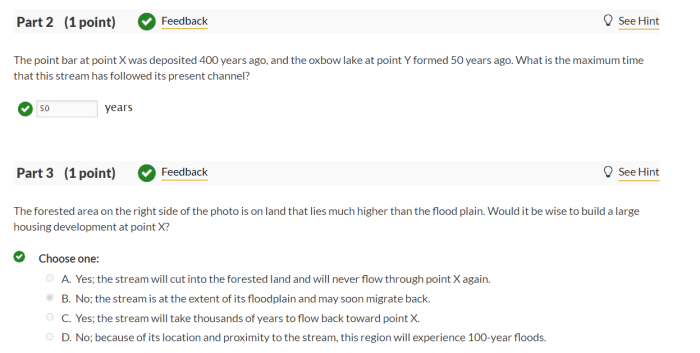
3. Discuss the Role of Fluvial Processes in Shaping the Landscape, Label all the features of this fluvial landscape.
Fluvial processes, including erosion, transportation, and deposition, shape the landscape:
Erosion
Erosion is the wearing away of land surfaces by flowing water. It occurs through hydraulic action, abrasion, and solution.
Transportation
Transportation is the movement of sediment by flowing water. It is influenced by sediment size, shape, and flow velocity.
Deposition
Deposition is the settling of sediment from flowing water. It occurs when flow velocity decreases, allowing sediment to settle out.
4. Explore the Ecological Importance of Fluvial Landscapes
Fluvial landscapes support diverse flora and fauna:
- Riparian Vegetation:Plants along river banks provide shade, stabilize banks, and filter pollutants.
- Aquatic Plants:Submerged and emergent plants provide food and shelter for aquatic organisms.
- Fish and Invertebrates:Rivers and associated wetlands support a wide range of fish and invertebrate species.
- Birds and Mammals:Riparian areas and floodplains provide important habitats for birds and mammals.
Fluvial systems also perform vital ecological functions:
- Nutrient Cycling:Rivers transport nutrients, supporting plant growth and ecosystem productivity.
- Water Filtration:Riparian vegetation and wetlands filter pollutants, improving water quality.
- Flood Control:Floodplains and wetlands absorb excess water, reducing flood damage.
5. Examine the Human Impact on Fluvial Landscapes
Human activities have significantly altered fluvial landscapes:
- Dams and Levees:Dams alter flow patterns, fragmenting habitats and disrupting sediment transport.
- Channelization:Straightening rivers reduces meandering, decreasing habitat diversity and increasing erosion.
- Agriculture and Urbanization:Land use changes can increase sediment and nutrient inputs, affecting water quality.
- Climate Change:Changes in precipitation patterns and temperature can alter flow regimes and increase flooding.
Sustainable management strategies are crucial to mitigate human impacts and preserve the ecological integrity of fluvial landscapes.
Frequently Asked Questions: Label All The Features Of This Fluvial Landscape.
What are the key characteristics of a fluvial landscape?
Fluvial landscapes are characterized by the presence of rivers, which are the primary agents of erosion, transportation, and deposition. They exhibit features such as meanders, oxbow lakes, floodplains, and terraces, which are shaped by the river’s flow and sediment load.
How do fluvial processes create different landforms?
Fluvial processes, including erosion, transportation, and deposition, work together to create a variety of landforms in fluvial landscapes. Erosion by the river’s current carves out channels and valleys, while sediment deposition forms features such as point bars, levees, and floodplains.
What is the ecological importance of fluvial landscapes?
Fluvial landscapes provide diverse habitats for a wide range of flora and fauna. The vegetation along riverbanks stabilizes the soil and provides food and shelter for animals. Floodplains serve as important breeding and feeding grounds for many species, and the river itself supports aquatic ecosystems.