Diffusion and osmosis ap bio lab – Diffusion and osmosis, fundamental processes in biology, govern the movement of molecules across membranes and play critical roles in cellular function. This article delves into the concepts, applications, and implications of these essential processes, providing an in-depth understanding for AP Biology students.
Diffusion, the passive movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration, and osmosis, the selective movement of water across a semipermeable membrane, are essential for nutrient transport, water balance, and homeostasis in living organisms.
Diffusion and Osmosis
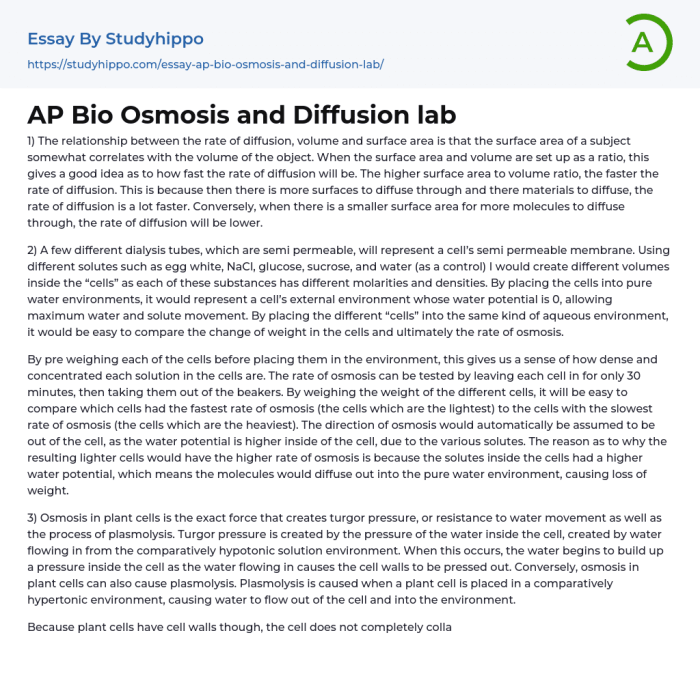
Diffusion and osmosis are two fundamental processes that drive the movement of molecules across biological membranes. These processes are essential for a wide range of cellular functions, including nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling.
Diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This process occurs passively, without the need for energy input. The rate of diffusion is determined by several factors, including the concentration gradient, the size of the molecules, and the temperature.
Osmosis
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane. A semipermeable membrane is a membrane that allows some molecules to pass through but blocks others. In the case of osmosis, water molecules can pass through the membrane, but solute molecules cannot.
This creates a concentration gradient, with water molecules moving from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Diffusion and Osmosis
The rate of diffusion and osmosis is affected by several factors, including:
- Concentration gradient:The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion and osmosis.
- Size of the molecules:Smaller molecules diffuse and osmose more quickly than larger molecules.
- Temperature:The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion and osmosis.
Applications of Diffusion and Osmosis in Biological Systems
Diffusion and osmosis play a vital role in a wide range of biological systems, including:
- Nutrient uptake:Diffusion and osmosis allow nutrients to enter cells from the surrounding environment.
- Waste removal:Diffusion and osmosis allow waste products to leave cells.
- Cell signaling:Diffusion and osmosis are involved in the transmission of chemical signals between cells.
Diffusion and Osmosis Lab
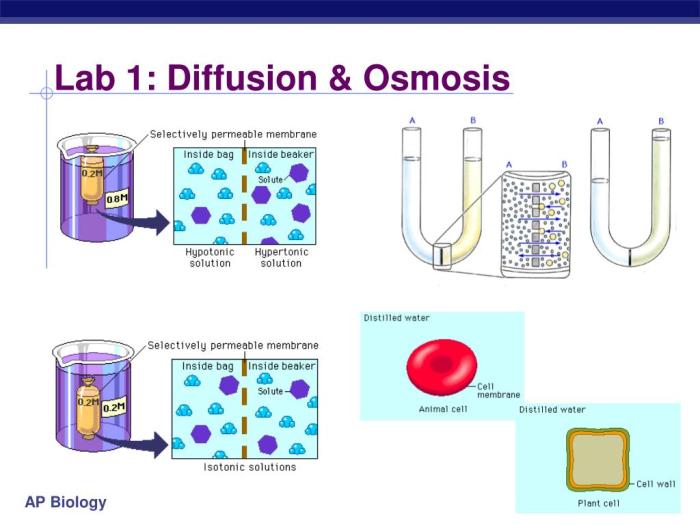
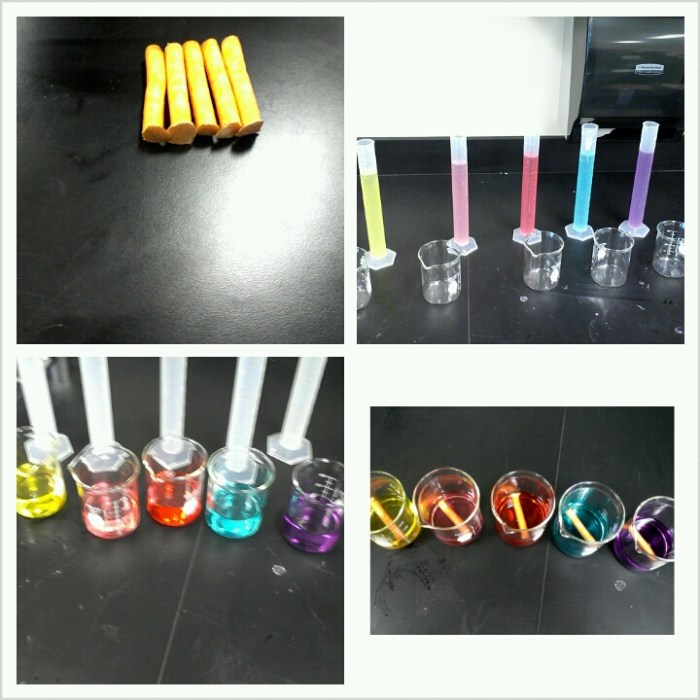
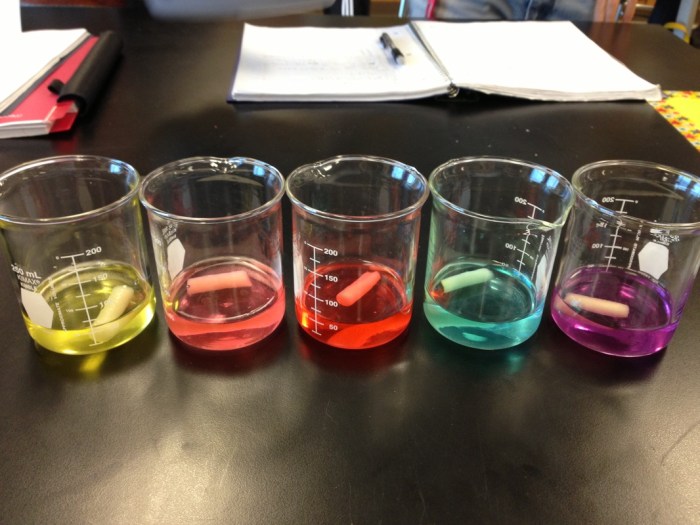
This lab aims to investigate the processes of diffusion and osmosis through hands-on experiments. It allows students to observe and analyze how molecules move across semipermeable membranes, which is crucial for understanding cellular processes and the functioning of living organisms.
Materials and Methods
The lab utilizes materials such as dialysis tubing, distilled water, salt solutions, and indicators. Students set up experimental setups where they place different substances inside the dialysis tubing and immerse them in various solutions. By monitoring changes in concentration and observing the movement of molecules, they gather data to analyze diffusion and osmosis.
Results
The lab results demonstrate that diffusion is the net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, driven by the concentration gradient. Osmosis, on the other hand, is the specific movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration, driven by the difference in solute concentration.
Implications
The implications of the lab results extend beyond the classroom. Diffusion and osmosis play vital roles in various biological processes, including nutrient transport, waste removal, and maintaining cell homeostasis. Understanding these processes is essential for comprehending the functioning of living organisms and for developing treatments for diseases that affect cellular processes.
Design an Experiment to Investigate Diffusion and Osmosis

Diffusion and osmosis are fundamental processes in biology that involve the movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane. Understanding the factors that influence the rates of diffusion and osmosis is essential for comprehending a wide range of biological phenomena. In this section, we will design experiments to investigate the effects of temperature, concentration, and surface area on the rates of diffusion and osmosis.
Effect of Temperature on the Rate of Diffusion
The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the temperature. This is because temperature increases the kinetic energy of molecules, causing them to move more rapidly and diffuse more quickly across the membrane.
To investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of diffusion, we can design an experiment using a diffusion chamber. The chamber is divided into two compartments by a semipermeable membrane. One compartment is filled with a solution of a colored dye, while the other compartment is filled with pure water.
The temperature of the chamber is then varied, and the rate of diffusion of the dye across the membrane is measured. We predict that the rate of diffusion will increase as the temperature increases.
Effect of Concentration on the Rate of Osmosis
The rate of osmosis is directly proportional to the concentration gradient across the membrane. This is because water molecules move from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration, in an attempt to equalize the concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
To investigate the effect of concentration on the rate of osmosis, we can design an experiment using an osmometer. The osmometer is a U-shaped tube with a semipermeable membrane separating the two arms of the tube. One arm of the tube is filled with a solution of a known concentration, while the other arm is filled with pure water.
The height of the water column in each arm of the tube is then measured. We predict that the height of the water column in the arm containing the solution will be higher than the height of the water column in the arm containing pure water, and that the difference in height will increase as the concentration of the solution increases.
Effect of Surface Area on the Rate of Diffusion, Diffusion and osmosis ap bio lab
The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the surface area of the membrane. This is because a larger surface area provides more space for molecules to diffuse across the membrane.
To investigate the effect of surface area on the rate of diffusion, we can design an experiment using a diffusion cell. The diffusion cell is a chamber with two compartments separated by a semipermeable membrane. The surface area of the membrane is varied, and the rate of diffusion of a gas across the membrane is measured.
We predict that the rate of diffusion will increase as the surface area of the membrane increases.
Applications of Diffusion and Osmosis in Biology: Diffusion And Osmosis Ap Bio Lab
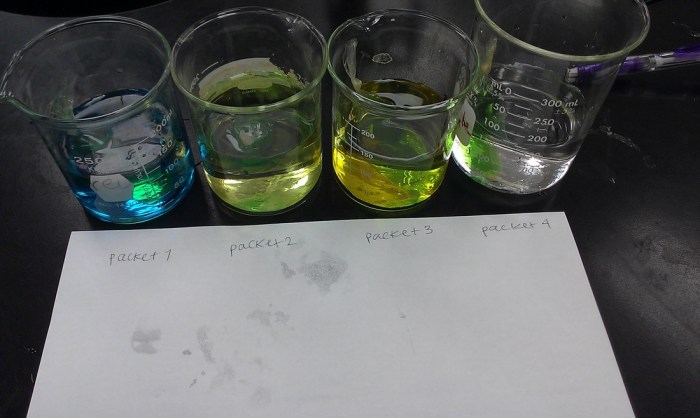

Diffusion and osmosis play crucial roles in various biological processes, enabling the transport of essential substances and maintaining the delicate balance within living organisms.
Role in Nutrient Transport
Diffusion facilitates the movement of nutrients, such as oxygen, glucose, and ions, into and out of cells. This exchange is essential for cellular metabolism, growth, and repair. Osmosis, on the other hand, enables the movement of water across semipermeable membranes, ensuring the proper hydration of cells and the transport of water-soluble nutrients.
Role in Water Balance Regulation
Diffusion and osmosis are critical in maintaining water balance in organisms. By regulating the movement of water between different compartments, these processes prevent cells from bursting or shrinking excessively. This balance is particularly important in plants, where turgor pressure, generated by osmosis, provides structural support and regulates stomatal opening for gas exchange.
Role in Homeostasis
Diffusion and osmosis contribute to the maintenance of homeostasis by facilitating the exchange of substances between cells and their surroundings. This exchange ensures that the internal environment of cells remains stable, despite changes in the external environment. For example, diffusion of carbon dioxide out of cells helps regulate pH levels, while osmosis regulates the distribution of water and solutes to maintain osmotic balance.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion involves the movement of all particles, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
What factors affect the rate of diffusion and osmosis?
Temperature, concentration gradient, surface area, and membrane permeability influence the rates of diffusion and osmosis.
What are some applications of diffusion and osmosis in biology?
Diffusion and osmosis are essential for nutrient uptake, waste removal, water balance, and maintaining homeostasis in organisms.

